Describing Character: Adjectives for Behaviour in English
Understanding how to use adjectives to describe behavior is crucial for effective communication in English. These adjectives allow us to express nuanced opinions, provide detailed character assessments, and vividly portray individuals’ actions and attitudes. Whether you’re writing a character analysis, giving feedback, or simply describing someone to a friend, mastering these adjectives will significantly enhance your descriptive abilities. This article explores the vast landscape of adjectives for behavior, providing definitions, examples, and practical exercises to help learners of all levels improve their vocabulary and grammatical accuracy.
This guide is tailored for English language learners aiming to refine their descriptive skills, writers seeking to create compelling characters, and anyone interested in expanding their vocabulary related to human behavior. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of various adjectives, their proper usage, and common pitfalls to avoid, enabling you to communicate with greater precision and confidence.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Adjectives for Behaviour
- Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
- Types and Categories of Behavioural Adjectives
- Examples of Adjectives for Behaviour
- Usage Rules for Adjectives of Behaviour
- Common Mistakes with Adjectives for Behaviour
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Definition of Adjectives for Behaviour
Adjectives for behavior are words that describe the way a person or animal acts. They provide insight into character, personality, and conduct. These adjectives are essential for painting a vivid picture of individuals and their interactions, adding depth and clarity to our communication. They allow us to judge, appreciate, or simply understand the actions of others and ourselves.
Functionally, adjectives for behavior modify nouns (people, animals, or abstract concepts like “conduct” or “demeanor”). They answer the question “What kind of person/behavior?” and provide details about specific qualities. These adjectives can be used in various contexts, including literature, everyday conversation, professional evaluations, and academic analyses. Understanding the nuances of these words can significantly impact how we perceive and describe the world around us.
Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
Adjectives, in general, typically precede the noun they modify (the kind man) or follow a linking verb, such as to be (He is kind). Adjectives for behaviour follow this same rule. They can be simple words (e.g., kind, rude), compound words (e.g., well-behaved, ill-mannered), or derived from other parts of speech, often by adding suffixes such as -ful (e.g., careful), -less (e.g., careless), -ive (e.g., aggressive), or -able (e.g., agreeable).
Many adjectives can also form comparative and superlative degrees to express varying levels of intensity. This is done either by adding -er and -est to the base form (e.g., kinder, kindest) or by using the words more and most (e.g., more considerate, most considerate). Understanding these structural elements helps in using adjectives accurately and effectively.
Types and Categories of Behavioural Adjectives
Adjectives for behavior can be broadly categorized based on the type of behavior they describe. Here are several key categories:
Positive Adjectives
These adjectives describe desirable or commendable behaviors. They often reflect qualities that are valued and admired in individuals and societies. Examples include:
- Kind
- Generous
- Helpful
- Considerate
- Polite
- Courteous
- Patient
- Responsible
- Diligent
- Honest
Negative Adjectives
These adjectives describe undesirable or unacceptable behaviors. They often indicate flaws or shortcomings in an individual’s character. Examples include:
- Rude
- Selfish
- Aggressive
- Impatient
- Irresponsible
- Dishonest
- Lazy
- Mean
- Cruel
- Disrespectful
Neutral Adjectives
These adjectives describe behaviors that are neither particularly positive nor negative. They often provide factual descriptions without expressing a strong opinion. Examples include:
- Quiet
- Reserved
- Observant
- Cautious
- Independent
- Practical
- Serious
- Conventional
- Formal
- Unpredictable
Adjectives of Intensity
These adjectives amplify or diminish the strength of a behavior. They can be used with both positive and negative adjectives to provide a more precise description. Examples include:
- Extremely kind
- Very rude
- Slightly aggressive
- Intensely patient
- Remarkably responsible
- Completely dishonest
- Mildly lazy
- Exceptionally mean
- Unusually cruel
- Incredibly disrespectful
Examples of Adjectives for Behaviour
The following tables provide examples of how adjectives for behavior can be used in sentences. Each table focuses on a different category of adjectives, illustrating their usage in various contexts.
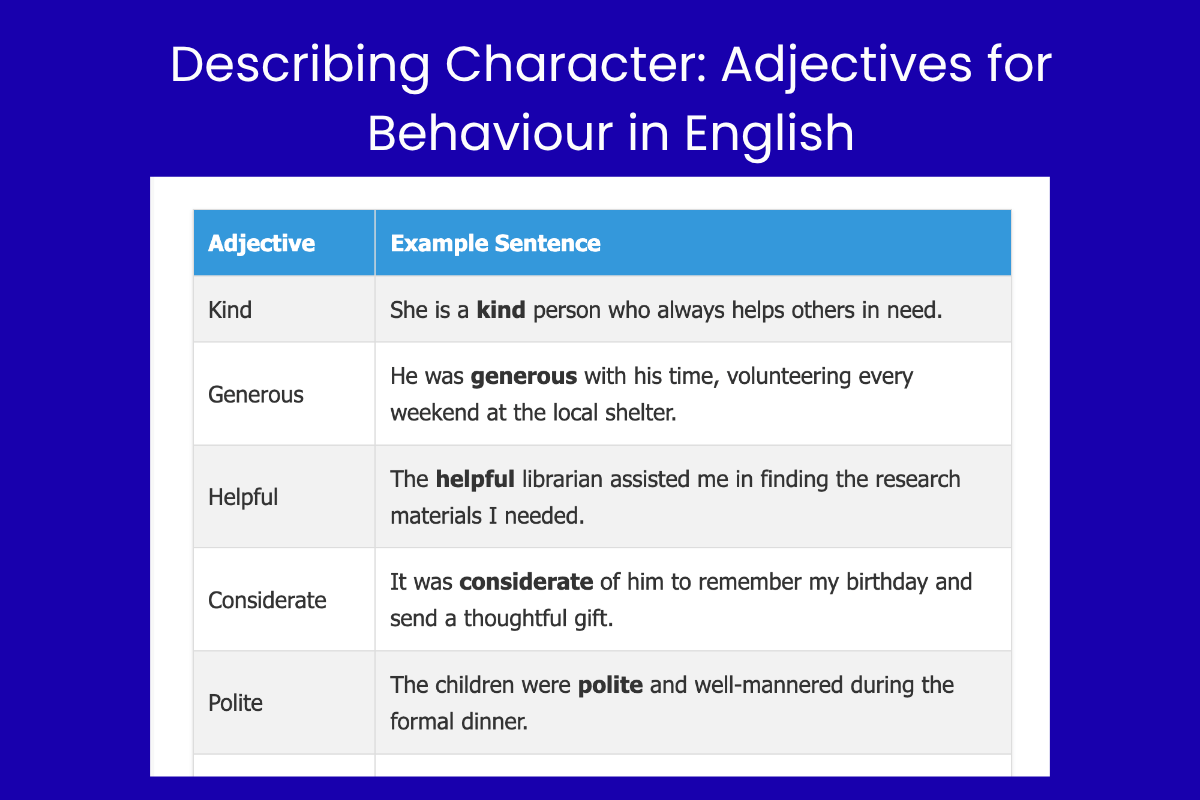
Positive Behaviour Examples
This table showcases examples of positive adjectives used to describe behavior. Notice how each adjective adds a specific positive attribute to the person or action being described.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Kind | She is a kind person who always helps others in need. |
| Generous | He was generous with his time, volunteering every weekend at the local shelter. |
| Helpful | The helpful librarian assisted me in finding the research materials I needed. |
| Considerate | It was considerate of him to remember my birthday and send a thoughtful gift. |
| Polite | The children were polite and well-mannered during the formal dinner. |
| Courteous | A courteous gentleman opened the door for her and offered his assistance. |
| Patient | The teacher was patient with the students who struggled to understand the concept. |
| Responsible | As a responsible employee, she always completed her tasks on time and with care. |
| Diligent | The diligent student spent hours studying to ensure she understood the material. |
| Honest | He is an honest businessman who always conducts his affairs with integrity. |
| Loyal | The dog was a loyal companion, always by his owner’s side. |
| Brave | The brave firefighter rescued the family from the burning building. |
| Cheerful | Her cheerful disposition brightened everyone’s day. |
| Compassionate | The nurse was compassionate towards her patients, providing comfort and care. |
| Cooperative | The team was cooperative, working together to achieve their goals. |
| Creative | The creative artist produced stunning works of art. |
| Decisive | The leader was decisive, making quick and effective decisions. |
| Empathetic | The therapist was empathetic, understanding and sharing her clients’ feelings. |
| Faithful | He was a faithful friend, always there in times of need. |
| Gentle | She had a gentle touch when caring for the injured bird. |
| Gracious | The host was gracious, making everyone feel welcome. |
| Humble | Despite his success, he remained humble and approachable. |
| Idealistic | The young activist was idealistic, striving for a better world. |
| Joyful | The children were joyful, playing in the park. |
| Loving | She was a loving mother, always putting her children first. |
| Mature | He showed mature behavior in handling the difficult situation. |
| Noble | The knight was a noble warrior, fighting for justice. |
| Optimistic | She had an optimistic outlook, always seeing the positive side. |
| Passionate | He was passionate about his work, dedicating himself fully. |
Negative Behaviour Examples
This table presents examples of negative adjectives used to describe behavior. These adjectives highlight undesirable traits and actions.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Rude | It was rude of him to interrupt the speaker during the presentation. |
| Selfish | Her selfish behavior alienated her from her friends and family. |
| Aggressive | The aggressive player was penalized for his violent conduct on the field. |
| Impatient | The impatient customer complained loudly about the slow service. |
| Irresponsible | His irresponsible actions led to serious consequences for the company. |
| Dishonest | The dishonest politician was caught in a scandal involving bribery. |
| Lazy | The lazy worker avoided his tasks and relied on others to do his job. |
| Mean | It was mean of her to spread rumors about her colleagues. |
| Cruel | The cruel dictator oppressed his people with harsh and inhumane laws. |
| Disrespectful | The students were disrespectful to the teacher, talking and laughing during the lesson. |
| Arrogant | His arrogant attitude made it difficult for others to work with him. |
| Boastful | He was boastful about his achievements, constantly bragging to others. |
| Careless | His careless driving caused an accident. |
| Deceitful | The deceitful salesman lied to customers to make a sale. |
| Envious | She was envious of her friend’s success. |
| Frivolous | His frivolous spending habits led to financial problems. |
| Greedy | The greedy businessman exploited his workers for profit. |
| Hateful | His hateful speech incited violence. |
| Ignorant | His ignorant remarks offended many people. |
| Jealous | She was jealous of her sister’s relationship. |
| Malicious | The malicious gossip spread quickly through the office. |
| Nasty | He made a nasty comment about her appearance. |
| Obnoxious | His obnoxious behavior was annoying to everyone. |
| Pessimistic | He had a pessimistic view of the future. |
| Quarrelsome | The couple was quarrelsome, always arguing. |
| Reckless | His reckless actions put others in danger. |
| Sarcastic | Her sarcastic remarks were often hurtful. |
| Thoughtless | It was thoughtless of him to forget her birthday. |
| Unkind | His unkind words made her cry. |
| Vain | She was vain about her appearance. |
Neutral Behaviour Examples
This table provides examples of neutral adjectives describing behavior, focusing on observations without strong positive or negative connotations.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Quiet | She is a quiet student who prefers to listen and observe. |
| Reserved | He is a reserved individual who doesn’t easily share his feelings. |
| Observant | The observant detective noticed subtle clues that others missed. |
| Cautious | She is cautious when making decisions, carefully considering all the options. |
| Independent | He is an independent worker who prefers to manage his own tasks. |
| Practical | She has a practical approach to problem-solving, focusing on realistic solutions. |
| Serious | He is a serious student who is dedicated to his studies. |
| Conventional | She has a conventional style, preferring traditional clothing and customs. |
| Formal | The meeting was conducted in a formal manner, with strict adherence to protocol. |
| Unpredictable | His behavior is unpredictable, making it difficult to anticipate his reactions. |
| Analytical | She has an analytical mind and enjoys solving complex problems. |
| Competent | He is a competent professional, capable of handling any task. |
| Disciplined | She is a disciplined athlete, adhering strictly to her training schedule. |
| Efficient | He is an efficient worker, completing tasks quickly and accurately. |
| Focused | She is focused on her goals, working diligently to achieve them. |
| Industrious | He is an industrious student, always working hard to succeed. |
| Logical | She has a logical approach to decision-making. |
| Methodical | He is methodical in his work, following a structured process. |
| Objective | She tries to be objective in her assessments, avoiding personal bias. |
| Organized | He is an organized person, keeping everything in its place. |
| Precise | She is precise in her measurements. |
| Rational | He is rational in his arguments. |
| Systematic | She is systematic in her approach. |
| Tidy | He is tidy in his habits. |
| Traditional | She is traditional in her views. |
| Unassuming | He is unassuming despite his achievements. |
| Versatile | She is versatile in her skills. |
| Wise | He is wise beyond his years. |
| Zealous | She is zealous in her pursuit. |
| Practical | He is practical in his thinking. |
Intensity Behaviour Examples
This table demonstrates how adjectives of intensity can modify other adjectives describing behavior, enhancing or diminishing their impact.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Extremely kind | She is extremely kind, always going above and beyond to help others. |
| Very rude | He was very rude to the waiter, snapping his fingers and demanding attention. |
| Slightly aggressive | He became slightly aggressive when he felt his ideas were being dismissed. |
| Intensely patient | The teacher was intensely patient with the struggling students, providing individualized support. |
| Remarkably responsible | She is remarkably responsible, always taking ownership of her actions and their consequences. |
| Completely dishonest | He was completely dishonest about his qualifications, fabricating his entire resume. |
| Mildly lazy | He was mildly lazy around the house, often leaving his chores unfinished. |
| Exceptionally mean | She was exceptionally mean to her younger siblings, constantly teasing and belittling them. |
| Unusually cruel | The punishment was unusually cruel, far exceeding the severity of the offense. |
| Incredibly disrespectful | He was incredibly disrespectful to his elders, ignoring their advice and talking back rudely. |
| Quite generous | He was quite generous with his donations to charity. |
| So helpful | She was so helpful when I was moving. |
| Terribly impatient | He was terribly impatient waiting in line. |
| Wonderfully polite | She was wonderfully polite to everyone she met. |
| Awfully quiet | He was awfully quiet during the meeting. |
| Somewhat reserved | She was somewhat reserved at first. |
| Deeply serious | He was deeply serious about his work. |
| Particularly observant | She was particularly observant of details. |
| Really cautious | He was really cautious in his decisions. |
| Super independent | She was super independent from a young age. |
| Slightly practical | He was slightly practical in his approach. |
| Moderately formal | The event was moderately formal. |
| Noticeably unpredictable | His behavior was noticeably unpredictable. |
| Extremely analytical | She was extremely analytical in her thinking. |
| Very competent | He was very competent in his role. |
| Incredibly disciplined | She was incredibly disciplined in her training. |
| Remarkably efficient | He was remarkably efficient at work. |
| Completely focused | She was completely focused on her studies. |
| Mildly industrious | He was mildly industrious around the house. |
| Exceptionally logical | She was exceptionally logical in her arguments. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives of Behaviour
Proper usage of adjectives is critical for clear and effective communication. Several key rules govern their application, including placement, comparative and superlative forms, order, and preposition combinations.
Adjective Placement
Adjectives typically precede the noun they modify. For example, “a kind man” or “generous donations.” However, adjectives can also follow linking verbs such as be, seem, appear, look, feel, taste, smell, and sound. For example, “He is kind” or “She seems generous.”
Comparative and Superlative Forms
Many adjectives can be used in comparative and superlative forms to show degrees of comparison. Short adjectives (usually one or two syllables) typically add -er for the comparative and -est for the superlative. For example, kinder and kindest. Longer adjectives usually use more and most. For example, more considerate and most considerate.
Irregular adjectives, such as good and bad, have irregular comparative and superlative forms (better and best; worse and worst, respectively).
Order of Adjectives
When using multiple adjectives to describe a noun, there is a general order to follow: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose. For example, “a beautiful large old round red Italian leather bag.” While this order is not always strictly followed, it provides a useful guideline for constructing grammatically correct and natural-sounding sentences.
Adjectives with Prepositions
Some adjectives commonly pair with specific prepositions to form idiomatic expressions. For example, “He is responsible for the project” or “She is kind to animals.” Knowing these combinations is essential for using adjectives correctly and naturally.
Here are some common adjectives for behavior paired with prepositions:
- Kind to
- Rude to
- Responsible for
- Aware of
- Good at
- Bad at
- Considerate of
Common Mistakes with Adjectives for Behaviour
Even advanced learners make mistakes with adjectives. Here are some frequent errors and how to correct them:
- Incorrect: He is more kinder than his brother.
Correct: He is kinder than his brother. - Incorrect: She is the most kindest person I know.
Correct: She is the kindest person I know. - Incorrect: He is responsible of the mistake.
Correct: He is responsible for the mistake. - Incorrect: She is a beautiful old red Italian large leather bag.
Correct: She is a beautiful large old red Italian leather bag. - Incorrect: He behaved badly.
Correct: He was ill-behaved. (or, He behaved badly.)
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of adjectives for behavior with the following exercises:
Exercise 1: Identifying Adjectives
Identify the adjectives for behavior in the following sentences:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The generous man donated a large sum to the charity. | Generous |
| 2. Her rude comments offended many people at the party. | Rude |
| 3. He is a responsible student who always completes his assignments on time. | Responsible |
| 4. The impatient driver honked his horn repeatedly in the traffic jam. | Impatient |
| 5. She is known for her kind and compassionate nature. | Kind, Compassionate |
| 6. The dishonest employee was fired for stealing from the company. | Dishonest |
| 7. His lazy attitude prevented him from achieving his goals. | Lazy |
| 8. The cautious investor carefully evaluated all the risks before making a decision. | Cautious |
| 9. The unpredictable weather made it difficult to plan outdoor activities. | Unpredictable |
| 10. He is a quiet and reserved individual who prefers solitude. | Quiet, Reserved |
Exercise 2: Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences with an appropriate adjective for behavior:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. It was very __________ of her to offer me her seat on the bus. | Kind/Considerate |
| 2. His __________ behavior at the meeting was completely unacceptable. | Rude/Disrespectful |
| 3. She is a very __________ person and always keeps her promises. | Responsible/Honest |
| 4. The __________ child refused to share his toys with the other children. | Selfish/Mean |
| 5. He is an __________ worker who always finishes his tasks efficiently. | Industrious/Diligent |
| 6. Her __________ nature makes her a great listener and friend. | Empathetic/Compassionate |
| 7. It’s important to be __________ when making important financial decisions. | Cautious/Prudent |
| 8. Despite his success, he remained __________ and humble. | Unassuming/Modest |
| 9. She has a very __________ approach to solving problems. | Practical/Logical |
| 10. His __________ behavior made it difficult to work with him. | Arrogant/Boastful |
Exercise 3: Rewriting Sentences
Rewrite the following sentences using a different adjective for behavior with a similar meaning:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. She is a kind person. | She is a compassionate person. |
| 2. He is a rude man. | He is a disrespectful man. |
| 3. She is a responsible employee. | She is a dependable employee. |
| 4. He is a lazy student. | He is an idle student. |
| 5. She is a quiet girl. | She is a reserved girl. |
| 6. He is a brave soldier. | He is a courageous soldier. |
| 7. She is a generous donor. | She is a charitable donor. |
| 8. He is a mean bully. | He is a cruel bully. |
| 9. She is a polite guest. | She is a courteous guest. |
| 10. He is an honest businessman. | He is a truthful businessman. |
Exercise 4: Error Correction
Correct the errors in the following sentences:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He is more kinder than his sister. | He is kinder than his sister. |
| 2. She is the most kindest person I know. | She is the kindest person I know. |
| 3. He is responsible of the mistake. | He is responsible for the mistake. |
| 4. She is a beautiful old red Italian large leather bag. | She is a beautiful large old red Italian leather bag. |
| 5. He behaved badly. | He was ill-behaved. OR He behaved badly (grammatically correct but less descriptive) |
| 6. It was very rudely of him to interrupt. | It was very rude of him to interrupt. |
| 7. She is a patientest teacher. | She is the most patient teacher. |
| 8. He is more responsible that his brother. | He is more responsible than his brother. |
| 9. She is kind with everyone. | She is kind to everyone. |
| 10. He is a very quietest person. | He is a very quiet person. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, understanding the nuances and idiomatic uses of adjectives for behavior can further refine their language skills.
Nuanced Meanings and Connotations
Many adjectives for behavior have subtle differences in meaning and connotation that can significantly impact the message conveyed. For example, while thrifty and cheap both describe someone careful with money, thrifty has a positive connotation of being resourceful, while cheap suggests stinginess.
Understanding these nuances requires exposure to a wide range of contexts and careful attention to how words are used by native speakers. Paying attention to the surrounding words and the overall tone of the communication can help discern the intended meaning.
Idiomatic Expressions
Idiomatic expressions involving adjectives for behavior add color and depth to the English language. These expressions often have meanings that are not immediately obvious from the individual words themselves.
Examples include:
- Good-natured: Having a pleasant and friendly disposition.
- Quick-tempered: Easily angered.
- Even-tempered: Calm and not easily angered.
- Strong-willed: Determined to do what one wants, even if others disagree.
- Well-behaved: Behaving in a polite or appropriate way.
Learning and using these expressions can make your English sound more natural and expressive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I choose the right adjective to describe someone’s behavior?
A: Consider the specific actions and attitudes you want to convey. Think about the context and the overall impression you want to create. Use a dictionary or thesaurus to explore synonyms and related words, paying attention to their nuances and connotations.
Q: Can an adjective for behavior have both positive and negative connotations?
A: Yes, some adjectives can be seen as positive or negative depending on the context. For example, aggressive can be positive in a competitive sports environment but negative in a social setting.
Q: How can I improve my vocabulary of adjectives for behavior?
A: Read widely, paying attention to how authors use adjectives to describe characters and their actions. Make flashcards with definitions and example sentences. Practice using new adjectives in your own writing and speaking.
Q: Are there any online resources for learning more about adjectives for behavior?
A: Yes, many websites and apps offer vocabulary-building exercises, quizzes, and interactive lessons. Online dictionaries and thesauruses can also provide definitions, synonyms, and examples of usage.
Q: How important is it to use adjectives for behavior correctly?
A: Using adjectives correctly is crucial for clear and effective communication. Incorrect usage can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and even offense. Accurate and precise language enhances your credibility and allows you to express your thoughts and ideas more effectively.
Conclusion
Mastering adjectives for behavior is an ongoing journey that enhances your ability to communicate effectively and expressively in English. By understanding the definitions, structural elements, types, and usage rules of these adjectives, you can paint vivid pictures of individuals’ actions and attitudes. Consistent practice, attention to nuance, and a willingness to learn from mistakes will help you refine your skills and communicate with greater precision and confidence. Whether you’re writing a novel, giving feedback, or simply describing someone to a friend, your enhanced vocabulary will undoubtedly enrich your communication.