Describing Tech: A Guide to Adjectives for Technology
In today’s world, technology plays a pivotal role in our daily lives. From smartphones to sophisticated AI systems, we constantly interact with various technological advancements. To effectively communicate about these technologies, a strong understanding of adjectives is essential. This article delves into the realm of adjectives specifically used to describe technology, covering their definitions, structures, usage rules, and common mistakes. Whether you’re a student, a tech enthusiast, or a professional, this guide will enhance your ability to articulate your thoughts on technology with precision and clarity.
This comprehensive guide is designed for anyone who wants to improve their English vocabulary related to technology. By understanding how to use adjectives effectively, you can express your opinions, describe features, and compare different technologies more accurately. This knowledge is invaluable in academic settings, professional environments, and everyday conversations.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Adjectives for Technology
- Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
- Types and Categories of Adjectives for Technology
- Examples of Adjectives for Technology
- Usage Rules for Adjectives
- Common Mistakes with Adjectives
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Definition of Adjectives for Technology
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. In the context of technology, adjectives are used to provide specific details about technological devices, systems, software, and related concepts. They help us understand the characteristics, features, and qualities of technology. Adjectives can describe the physical attributes of a device (e.g., sleek design), its performance capabilities (e.g., powerful processor), or its overall impact (e.g., innovative solution).
The function of adjectives is to add detail and specificity to our language, making it more descriptive and engaging. They allow us to paint a clearer picture of the technology we are discussing, enabling others to understand our perspective and opinions. In the context of technology, adjectives are crucial for conveying information accurately and effectively, whether in technical documentation, marketing materials, or everyday conversations.
Adjectives for technology can be classified based on their function. Some describe physical attributes (e.g., lightweight, compact), others describe performance (e.g., efficient, reliable), and still others express opinions or evaluations (e.g., user-friendly, cutting-edge). Understanding these different categories can help you choose the most appropriate adjective for a given context.
Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
Adjectives in English typically precede the noun they modify. For instance, in the phrase “advanced technology,” the adjective “advanced” comes before the noun “technology.” However, adjectives can also follow linking verbs such as “is,” “are,” “was,” “were,” “seems,” and “becomes.” For example, “The software is intuitive.”
Many adjectives are formed by adding suffixes to nouns or verbs. Common suffixes include “-able,” “-ible,” “-ive,” “-al,” “-ic,” “-ous,” and “-ful.” For example, “access” (noun) becomes “accessible” (adjective), and “create” (verb) becomes “creative” (adjective). Recognizing these patterns can help you expand your vocabulary and understand the meaning of unfamiliar adjectives.
Adjectives can also be modified by adverbs to indicate the degree or intensity of the quality they describe. For example, “very powerful” or “extremely user-friendly.” Adverbs like “very,” “extremely,” “slightly,” and “relatively” can significantly alter the meaning of an adjective, allowing for more nuanced descriptions.
Types and Categories of Adjectives for Technology
Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives provide factual information about the characteristics of technology. They describe physical attributes, features, and specifications. These adjectives are often objective and can be verified through observation or measurement. Examples include digital, wireless, portable, ergonomic, and high-resolution.
Descriptive adjectives are essential for providing clear and precise information about technology. They help users understand the technical specifications and capabilities of a device or system. For example, describing a monitor as “high-resolution” indicates its image quality, while describing a laptop as “portable” highlights its ease of transport.
Evaluative Adjectives
Evaluative adjectives express opinions or judgments about the quality or performance of technology. They are subjective and reflect the speaker’s or writer’s perspective. Examples include innovative, reliable, user-friendly, efficient, groundbreaking, and obsolete.
Evaluative adjectives are crucial for expressing your opinions and assessments of technology. They help you convey your satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a particular device or system. For example, describing a software program as “user-friendly” indicates that it is easy to use, while describing a technology as “obsolete” suggests that it is outdated and no longer relevant.
Technical Adjectives
Technical adjectives are specific to the field of technology and are often used in technical documentation, specifications, and discussions among experts. They relate to particular functions, processes, or standards. Examples include bandwidth-intensive, cloud-based, AI-powered, open-source, cyber-secure, and quantum.
Technical adjectives are essential for precise communication within the tech industry. They allow professionals to convey complex information accurately and efficiently. For example, describing an application as “bandwidth-intensive” indicates that it requires a significant amount of network bandwidth, while describing a system as “cyber-secure” highlights its protection against cyber threats.
Examples of Adjectives for Technology
The following sections provide extensive examples of adjectives used to describe technology, organized by category. Each table includes a variety of adjectives with example sentences to illustrate their usage.
Descriptive Adjectives Examples
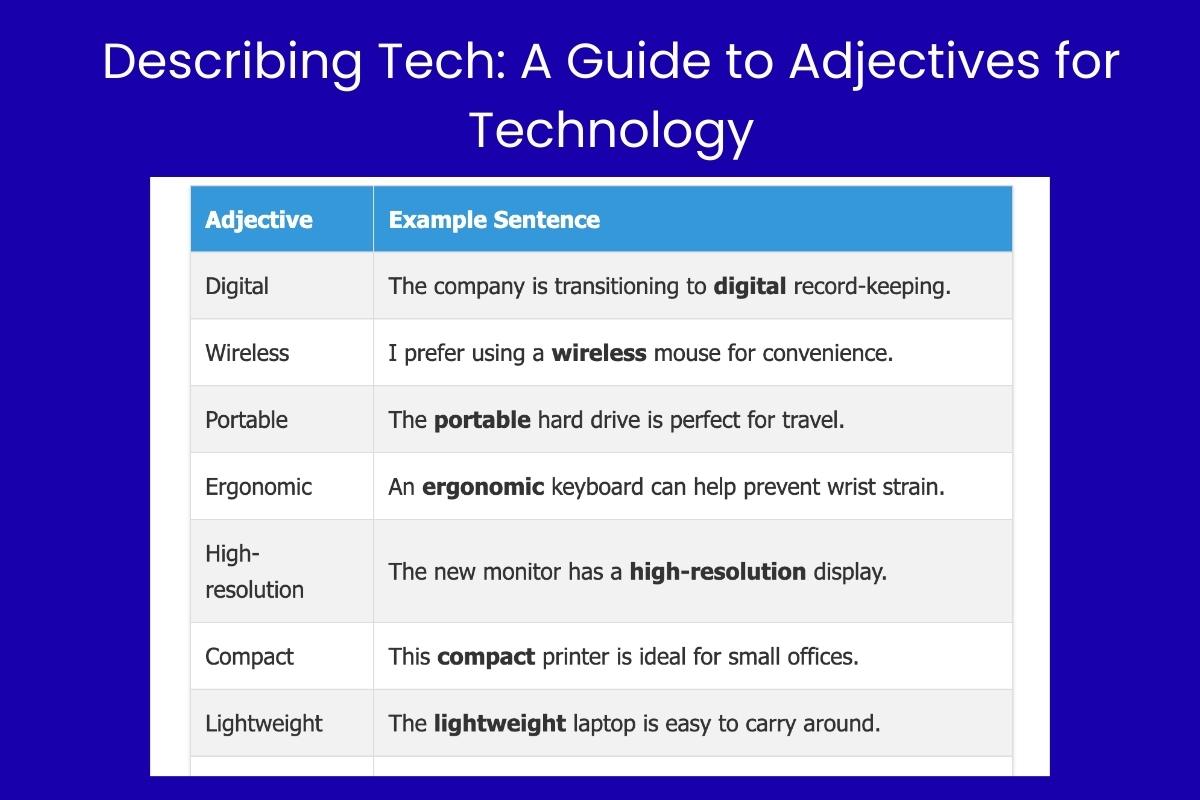
This table provides examples of descriptive adjectives used in the context of technology. These adjectives offer factual information about the characteristics of technological devices, systems, and software.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Digital | The company is transitioning to digital record-keeping. |
| Wireless | I prefer using a wireless mouse for convenience. |
| Portable | The portable hard drive is perfect for travel. |
| Ergonomic | An ergonomic keyboard can help prevent wrist strain. |
| High-resolution | The new monitor has a high-resolution display. |
| Compact | This compact printer is ideal for small offices. |
| Lightweight | The lightweight laptop is easy to carry around. |
| Advanced | The advanced security system protects the data. |
| Interactive | The interactive whiteboard enhances classroom engagement. |
| Automated | The factory uses automated assembly lines. |
| Electronic | He repaired the electronic circuit board. |
| Mechanical | The old typewriter was a mechanical marvel. |
| Optical | The optical drive reads CDs and DVDs. |
| Magnetic | The data was stored on a magnetic tape. |
| Acoustic | The acoustic sensors detected subtle sounds. |
| Virtual | We attended a virtual conference last week. |
| Augmented | The app uses augmented reality to enhance the experience. |
| Analog | The old radio used analog signals. |
| Embedded | The car has an embedded navigation system. |
| Networked | The networked computers share resources efficiently. |
| Smart | The smart thermostat learns your preferences. |
| Touchscreen | The touchscreen interface is very intuitive. |
| Programmable | The programmable robot can perform complex tasks. |
| Miniature | The miniature drone is perfect for indoor use. |
| Foldable | The foldable smartphone is easy to pocket. |
| Modular | The modular computer allows for easy upgrades. |
Evaluative Adjectives Examples
This table showcases evaluative adjectives that express opinions or judgments about technology. These adjectives reflect personal perspectives on the quality and performance of various technological devices and systems.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Innovative | The new smartphone has an innovative design. |
| Reliable | This software is very reliable and rarely crashes. |
| User-friendly | The new app is incredibly user-friendly. |
| Efficient | The efficient algorithm speeds up the process. |
| Groundbreaking | This technology is groundbreaking and will change the world. |
| Obsolete | That computer is now obsolete and needs to be replaced. |
| Sophisticated | The sophisticated system can handle complex tasks. |
| Cutting-edge | The laboratory uses cutting-edge research equipment. |
| State-of-the-art | The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art technology. |
| Impressive | The graphics card delivers impressive performance. |
| Advanced | The advanced AI is capable of learning. |
| Exceptional | The camera takes exceptional photographs. |
| Outstanding | The software has outstanding features. |
| Remarkable | The robot demonstrated remarkable agility. |
| Superior | The new model offers superior performance. |
| Inferior | This cheaper version is clearly inferior. |
| Subpar | The audio quality was subpar for a device of that price. |
| Unreliable | The connection is unreliable and often drops. |
| Inefficient | The old program is inefficient and slow. |
| Cumbersome | The device is cumbersome to operate. |
| Difficult | The software is difficult to navigate. |
| Challenging | The project presented challenging technical hurdles. |
| Complex | The system is complex but powerful. |
| Simple | The app has a simple and intuitive interface. |
| Intuitive | The design is very intuitive to use. |
Technical Adjectives Examples
This table provides a selection of technical adjectives commonly used in the field of technology. These adjectives are often found in technical documentation, specifications, and discussions among experts.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth-intensive | Streaming video is a bandwidth-intensive activity. |
| Cloud-based | The company uses a cloud-based storage solution. |
| AI-powered | The new software is AI-powered and learns from user behavior. |
| Open-source | The project is open-source and available for anyone to use. |
| Cyber-secure | The system is cyber-secure and protects against threats. |
| Quantum | Researchers are exploring quantum computing technologies. |
| Biometric | The phone uses biometric authentication for security. |
| Cryptographic | The data is protected by cryptographic algorithms. |
| Virtualized | The servers are virtualized to improve efficiency. |
| Scalable | The architecture is scalable to handle increasing demand. |
| Multithreaded | The application is multithreaded for better performance. |
| Real-time | The system provides real-time data updates. |
| High-speed | The network connection is high-speed and reliable. |
| Low-latency | The game requires a low-latency connection. |
| Energy-efficient | The appliance is energy-efficient and saves power. |
| Data-driven | The decision-making process is data-driven. |
| Software-defined | The network is software-defined for greater flexibility. |
| Hardware-accelerated | The graphics are hardware-accelerated for smoother rendering. |
| Internet-enabled | The device is Internet-enabled and connects to the web. |
| Network-centric | The architecture is network-centric and focuses on connectivity. |
| Platform-agnostic | The application is platform-agnostic and runs on any OS. |
| Server-side | The logic is implemented on the server-side. |
| Client-side | The rendering is done on the client-side. |
| API-driven | The integration is API-driven for seamless communication. |
| Machine-learning | The model is machine-learning based. |
| Deep-learning | The system uses deep-learning algorithms. |
| Blockchain-based | The application is blockchain-based. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives
Order of Adjectives
When using multiple adjectives to describe a noun, they typically follow a specific order. While not always rigid, the general order is: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose. For example, “a beautiful (opinion) large (size) old (age) round (shape) blue (color) Italian (origin) leather (material) computer (purpose) case.”
Understanding the order of adjectives can help you construct grammatically correct and natural-sounding sentences. While native speakers often follow this order intuitively, it’s helpful for learners to be aware of the general guidelines. When in doubt, try rearranging the adjectives to see which order sounds most natural.
Comparative and Superlative Forms
Adjectives have comparative and superlative forms to indicate degrees of quality. Comparative adjectives compare two things (e.g., “faster,” “more efficient”), while superlative adjectives compare three or more things (e.g., “fastest,” “most efficient”). For most one-syllable adjectives, add “-er” for the comparative and “-est” for the superlative. For longer adjectives, use “more” for the comparative and “most” for the superlative.
For example, “This processor is faster than the old one,” and “This is the fastest processor on the market.” Similarly, “This software is more user-friendly than the previous version,” and “This is the most user-friendly software available.” Some adjectives have irregular comparative and superlative forms (e.g., “good,” “better,” “best”).
Adjectives with Nouns
Adjectives typically precede the noun they modify. However, they can also follow linking verbs such as “is,” “are,” “was,” “were,” “seems,” and “becomes.” When adjectives follow linking verbs, they describe the subject of the sentence rather than directly modifying a noun.
For example, “The new phone is expensive” (adjective follows a linking verb) versus “The expensive phone has many features” (adjective precedes the noun). The choice of placement can affect the emphasis and flow of the sentence.
Common Mistakes with Adjectives
One common mistake is using adjectives as adverbs or vice versa. Adjectives modify nouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. For example, the correct sentence is “The program runs efficiently” (adverb), not “The program runs efficient” (adjective). Another error is incorrect adjective order, such as saying “a blue large screen” instead of “a large blue screen.”
Another frequent mistake involves using the base form of an adjective when the comparative or superlative form is required. For example, “This computer is good than that one” is incorrect; the correct sentence is “This computer is better than that one.” Additionally, learners sometimes misuse articles with adjectives, such as saying “I have a best phone” instead of “I have the best phone.”
Here are some examples of common mistakes and their corrections:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| The software is easy. | The software is easily used. | “Easy” is an adjective, but here, we need the adverb “easily” to modify the verb “used.” A better phrasing would be “The software is easy to use.” |
| A red big button. | A big red button. | Adjectives of size usually come before adjectives of color. |
| This is the good phone. | This is the best phone. | “Good” is the base form; “best” is the superlative form needed here. |
| This phone is more better. | This phone is better. | Do not use “more” with adjectives that already have “-er” in the comparative form. |
| An user-friendly app. | A user-friendly app. | Use “a” before consonant sounds and “an” before vowel sounds. Although “user” starts with a vowel letter, it has a consonant sound. |
Practice Exercises
The following exercises will help you practice using adjectives for technology. Each exercise focuses on a different aspect of adjective usage, from identifying adjectives to using them in sentences and forming comparative and superlative forms.
Exercise 1: Identifying Adjectives
Identify the adjectives in the following sentences. Some sentences may have more than one adjective.
| # | Sentence | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The innovative technology is changing the world. | innovative |
| 2 | The wireless mouse is very convenient. | wireless, convenient |
| 3 | This portable device is lightweight and compact. | portable, lightweight, compact |
| 4 | The advanced system requires complex programming. | advanced, complex |
| 5 | The old computer is now obsolete. | old, obsolete |
| 6 | We use a cloud-based storage solution. | cloud-based |
| 7 | The cyber-secure network protects against threats. | cyber-secure |
| 8 | The ergonomic keyboard prevents wrist strain. | ergonomic |
| 9 | The high-resolution display is very clear. | high-resolution |
| 10 | The user-friendly interface makes it easy to use. | user-friendly |
Exercise 2: Using Adjectives in Sentences
Fill in the blanks with appropriate adjectives from the list below. Use each adjective only once.
Adjective List: digital, reliable, efficient, automated, virtual, technical, impressive, scalable, quantum, cutting-edge
| # | Sentence | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The company is transitioning to ________ record-keeping. | digital |
| 2 | This software is very ________ and rarely crashes. | reliable |
| 3 | The ________ algorithm speeds up the process. | efficient |
| 4 | The factory uses ________ assembly lines. | automated |
| 5 | We attended a ________ conference last week. | virtual |
| 6 | The ________ documentation provides detailed information. | technical |
| 7 | The graphics card delivers ________ performance. | impressive |
| 8 | The architecture is ________ to handle increasing demand. | scalable |
| 9 | Researchers are exploring ________ computing technologies. | quantum |
| 10 | The laboratory uses ________ research equipment. | cutting-edge |
Exercise 3: Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Complete the sentences using the comparative or superlative form of the adjective in parentheses.
| # | Sentence | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | This new laptop is ________ (light) than my old one. | lighter |
| 2 | This is the ________ (efficient) program I have ever used. | most efficient |
| 3 | The new system is ________ (user-friendly) than the previous version. | more user-friendly |
| 4 | This is the ________ (advanced) technology available on the market. | most advanced |
| 5 | The ________ (good) solution is to upgrade the hardware. | best |
| 6 | The new phone is ________ (expensive) than I expected. | more expensive |
| 7 | This is the ________ (powerful) processor we have ever tested. | most powerful |
| 8 | The software is ________ (reliable) now than it was before the update. | more reliable |
| 9 | This is the ________ (complex) system I have ever worked with. | most complex |
| 10 | The new model is ________ (compact) than the old one. | more compact |
Advanced Topics
Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives are formed by combining two or more words, often with a hyphen. They function as a single adjective to modify a noun. Examples include “state-of-the-art” technology, “user-friendly” interface, and “high-speed” internet. Compound adjectives can add specificity and detail to your descriptions.
When forming compound adjectives, it’s important to use hyphens correctly. Generally, hyphenate compound adjectives that come before the noun they modify. For example, “a user-friendly design.” However, do not hyphenate them when they follow a linking verb. For example, “The design is user friendly.”
Participle Adjectives
Participle adjectives are formed from verbs using either the present participle (-ing) or the past participle (-ed). They function as adjectives to describe nouns. Examples include “cutting-edge” technology (present participle) and “cloud-based” storage (past participle). Participle adjectives can add dynamism and vividness to your descriptions.
Present participle adjectives often describe something that is actively causing an effect or performing an action. For example, “leading-edge” technology is actively pushing the boundaries of innovation. Past participle adjectives, on the other hand, often describe something that has been acted upon or has a particular state as a result. For example, “networked” computers are connected to a network.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between descriptive and evaluative adjectives?
Descriptive adjectives provide factual information about the characteristics of technology, such as “digital,” “wireless,” or “high-resolution.” They are objective and can be verified. Evaluative adjectives, on the other hand, express opinions or judgments about the quality or performance of technology, such as “innovative,” “reliable,” or “user-friendly.” They are subjective and reflect personal perspectives.
-
How do I use comparative and superlative adjectives correctly?
Comparative adjectives compare two things, while superlative adjectives compare three or more things. For most short adjectives, add “-er” for the comparative and “-est” for the superlative (e.g., “faster,” “fastest”). For longer adjectives, use “more” for the comparative and “most” for the superlative (e.g., “more efficient,” “most efficient”). Some adjectives have irregular forms (e.g., “good,” “better,” “best”).
-
What is the correct order of adjectives when using multiple adjectives to describe a noun?
The general order of adjectives is: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose. For example, “a beautiful large old round blue Italian leather computer case.” While this order is not always rigid, it provides a useful guideline for constructing grammatically correct and natural-sounding sentences.
-
What are compound adjectives, and how do I use them correctly?
Compound adjectives are formed by combining two or more words, often with a hyphen. They function as a single adjective to modify a noun. Hyphenate compound adjectives that come before the noun they modify (e.g., “a user-friendly design”), but do not hyphenate them when they follow a linking verb (e.g., “The design is user friendly”).
-
What are participle adjectives, and how are they formed?
Participle adjectives are formed from verbs using either the present participle (-ing) or the past participle (-ed). They function as adjectives to describe nouns. Present participle adjectives often describe something that is actively causing an effect (e.g., “cutting-edge” technology), while past participle adjectives often describe something that has been acted upon (e.g., “cloud-based” storage).
-
How can I avoid common mistakes when using adjectives?
Avoid using adjectives as adverbs or vice versa. Ensure that adjectives modify nouns and adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Pay attention to the correct order of adjectives when using multiple adjectives. Use the correct comparative or superlative form of adjectives when needed. Double-check your sentences to ensure that you are using adjectives correctly.
-
Where can I find more examples of adjectives used in the context of technology?
You can find examples of adjectives used in the context of technology in various sources, such as technical documentation, product reviews, news articles, and online forums. Pay attention to how native speakers and professional writers use adjectives to describe technology, and try to incorporate those patterns into your own writing and speaking.
-
Is there a difference between “technical” and “technological” adjectives?
Yes, while both relate to technology, they have slightly different nuances. “Technical” refers to the specific skills, knowledge, or procedures used in a field. For example, “technical specifications” or “technical support.” “Technological” refers more broadly to technology itself and its impact or characteristics. For example, “technological advancements” or “technological innovation.”
Conclusion
Mastering the use of adjectives for technology is crucial for effective communication in today’s tech-driven world. By understanding the different types of adjectives, their structure, and usage rules, you can express your thoughts and opinions about technology with greater precision and clarity. Remember to pay attention to adjective order, comparative and superlative forms, and common mistakes to enhance your fluency and accuracy.
This article has provided a comprehensive guide to adjectives for technology, covering definitions, examples, usage rules, and practice exercises. By consistently practicing and applying these concepts, you can significantly improve your ability to describe and discuss technology in English. Continue to explore new adjectives and expand your vocabulary to become a more confident and articulate communicator in the field of technology.
Keep practicing, and don’t be afraid to experiment with different adjectives to find the perfect words to describe the ever-evolving world of technology. With dedication and effort, you can master the art of using adjectives to communicate effectively about technology.